How To Grow Pot

Growing pot, more commonly known as cultivating cannabis, is a popular and increasingly legal activity with a rich history and a wide range of applications. Whether for medicinal or recreational purposes, cultivating cannabis requires a deep understanding of the plant's biology, ideal environmental conditions, and specific cultivation techniques. This guide aims to provide an in-depth exploration of the key aspects of growing pot, from selecting the right strain to harvesting and curing the final product.
Understanding Cannabis Biology and Strains
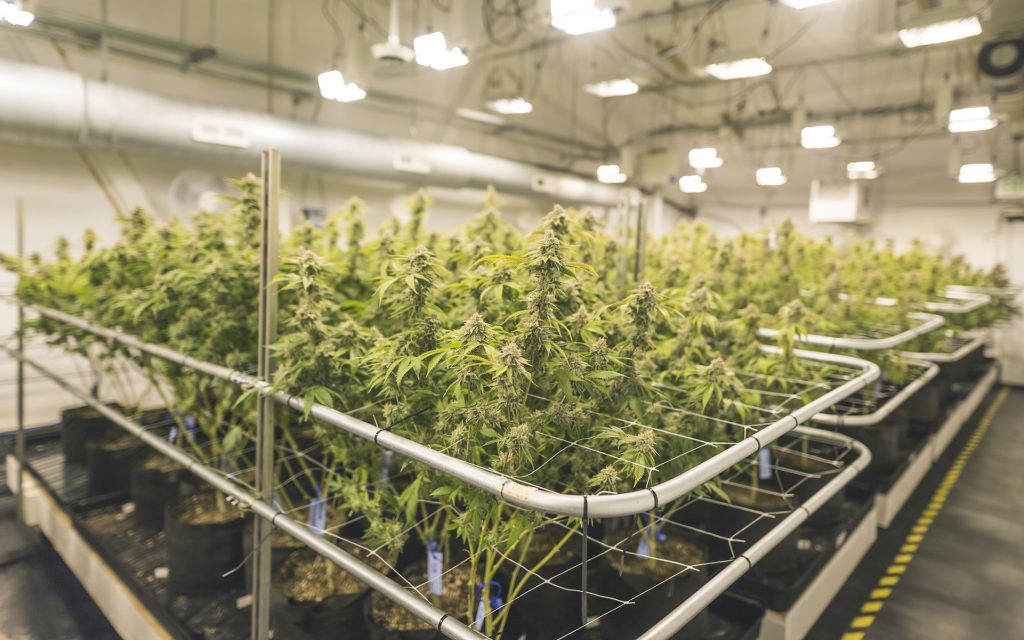

Before diving into the cultivation process, it's crucial to grasp the fundamental biology of the cannabis plant. Cannabis is an annual herb that exhibits dioecious characteristics, meaning it has separate male and female plants. This distinction is vital as it determines the plant's ability to produce flowers and, consequently, the valuable cannabinoids and terpenes sought after by cultivators and consumers alike.
The Importance of Strain Selection
Choosing the right cannabis strain is the first critical step in successful cultivation. Strains can be broadly categorized into indica, sativa, and hybrid varieties, each with its unique characteristics and effects. For instance, indica strains are typically shorter and bushier, with a higher concentration of the cannabinoid CBD, which is often associated with a relaxing and sedative effect. In contrast, sativa strains tend to be taller and slender, producing an energizing and uplifting effect due to their higher THC content.
Hybrid strains, as the name suggests, are a cross between indica and sativa plants, offering a blend of their respective traits. The choice of strain will depend on personal preferences, local climate conditions, and the cultivator's level of experience. Some popular strains include OG Kush, known for its potent and earthy flavor, Blue Dream, a balanced hybrid with a sweet and fruity aroma, and Northern Lights, an indica-dominant strain renowned for its relaxing and euphoric effects.
Creating the Optimal Growing Environment
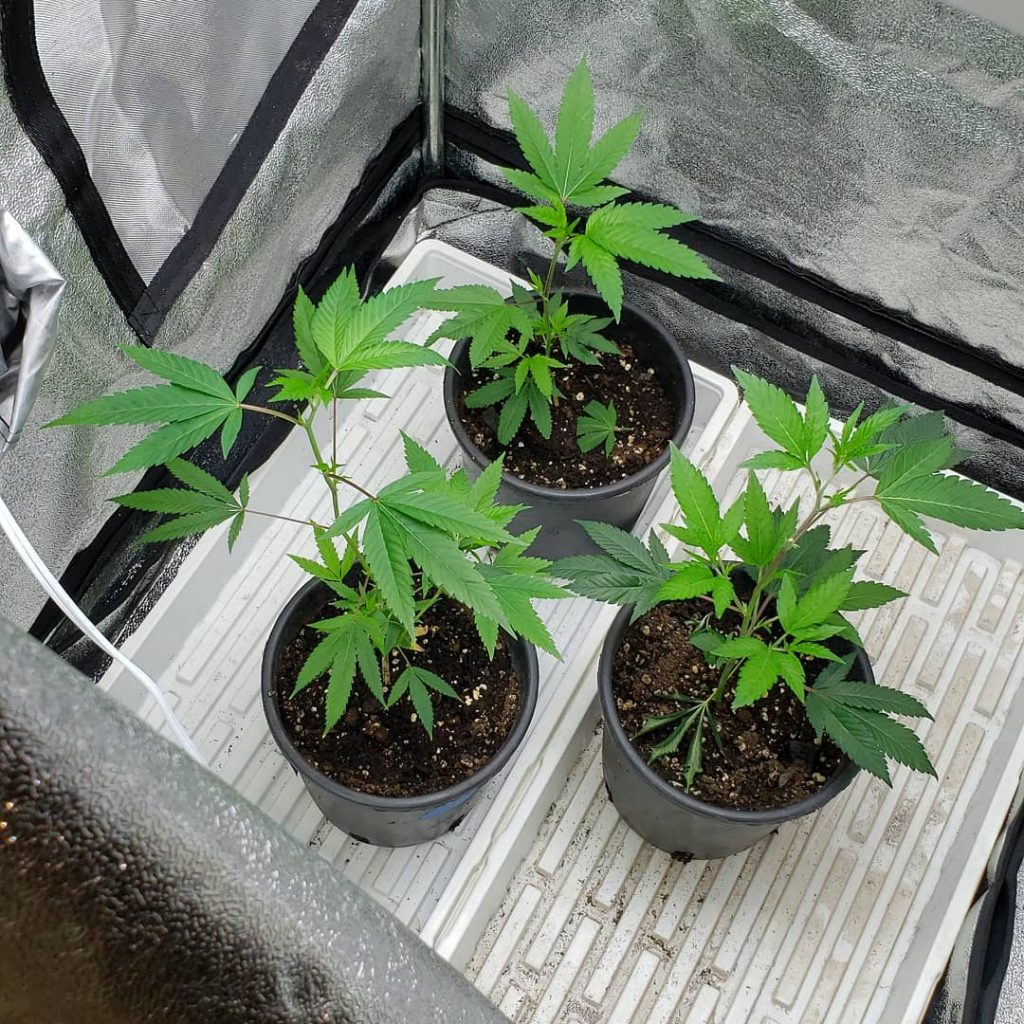

Cannabis plants thrive in specific environmental conditions, and replicating these conditions is essential for successful cultivation. Key factors to consider include temperature, humidity, light, and soil or growing medium.
Temperature and Humidity Control
Cannabis plants prefer a relatively stable temperature range, typically between 70°F and 85°F (21°C to 29°C) during the day and slightly cooler at night. Maintaining a consistent temperature helps prevent stress and promotes healthy growth. Humidity levels should be carefully managed, as cannabis is susceptible to mold and mildew if the environment is too damp. During the vegetative stage, a humidity range of 40% to 70% is ideal, while during flowering, it's best to keep humidity between 40% and 50% to prevent bud rot.
Lighting Requirements
Light is a critical factor in cannabis cultivation, as it drives the plant's growth and development. Cannabis plants require a minimum of 18 hours of light during the vegetative stage and 12 hours during the flowering stage. High-intensity discharge (HID) lamps, such as metal halide (MH) and high-pressure sodium (HPS) lights, are commonly used to provide the necessary light spectrum and intensity. LED lights are also gaining popularity due to their energy efficiency and ability to emit specific light wavelengths tailored to the plant's needs.
Soil and Growing Medium
The choice of growing medium can significantly impact the plant's health and yield. Cannabis can be grown in soil, soilless mixes, or hydroponically. Soil provides a natural and forgiving environment, offering a buffer against over-fertilization and helping to retain moisture. Soilless mixes, such as coco coir or perlite, offer better drainage and aeration, reducing the risk of root rot. Hydroponic systems, on the other hand, deliver nutrients directly to the plant's roots, resulting in faster growth and higher yields, but require more precise control and monitoring.
Cultivation Techniques and Best Practices
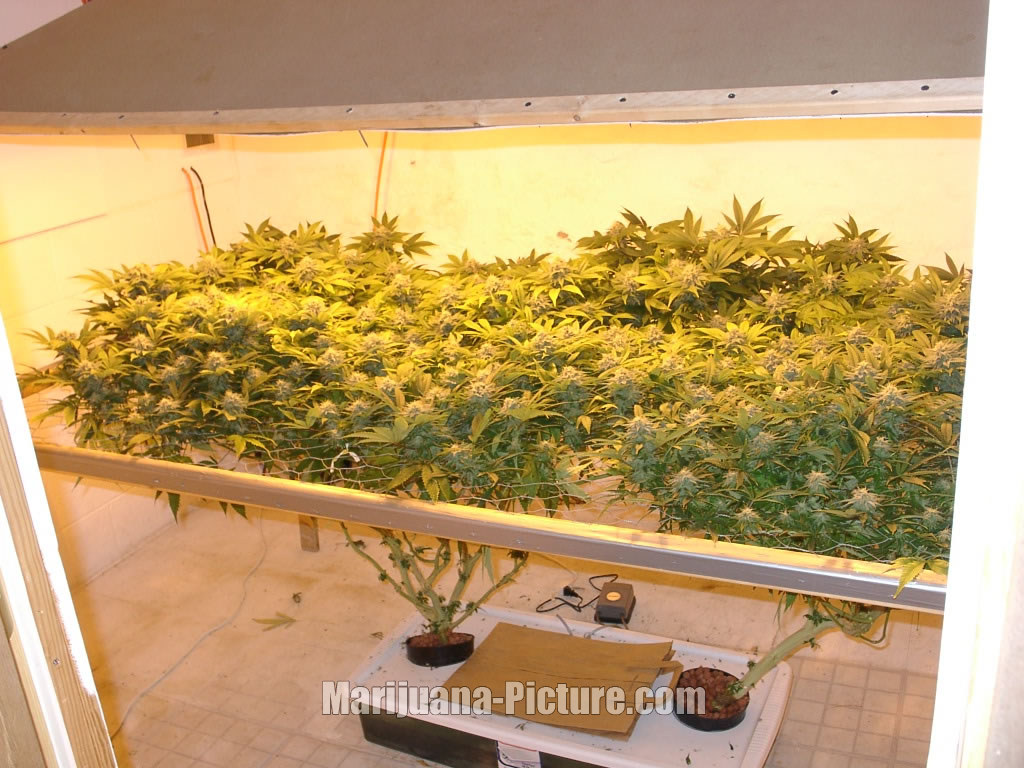

Once the optimal growing environment is established, various cultivation techniques can be employed to maximize the plant's potential. These techniques include proper watering, nutrient management, training and pruning, and pest and disease control.
Watering and Nutrient Management
Cannabis plants require consistent and adequate watering to thrive. Overwatering can lead to root rot, while underwatering can cause stress and nutrient deficiencies. The frequency and amount of water required will depend on the plant's size, the growing medium, and environmental conditions. Nutrient management is equally important, as cannabis plants require a balanced diet of macro and micronutrients throughout their life cycle. Common nutrients include nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK), as well as secondary and micronutrients like calcium, magnesium, and iron.
Training and Pruning
Training and pruning are essential techniques to maximize light penetration and airflow, encouraging robust growth and healthy buds. Common training methods include topping, which involves removing the top of the main stem to encourage lateral growth, and LST (Low-Stress Training), which uses gentle bending and tying to manipulate the plant's growth pattern. Pruning involves removing fan leaves and small branches to increase light penetration and direct the plant's energy towards bud development. It's important to avoid over-pruning, as this can stress the plant and reduce overall yield.
Pest and Disease Control
Cannabis plants are susceptible to a range of pests and diseases, including spider mites, aphids, powdery mildew, and root rot. Regular monitoring and early intervention are crucial to prevent infestations and infections. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies, such as biological control (using beneficial insects or microorganisms), cultural control (maintaining optimal growing conditions), and physical control (such as using barriers or traps), can effectively manage pest and disease issues without resorting to chemical pesticides.
Harvesting and Curing Cannabis

The final stage of the cultivation process is harvesting and curing the cannabis flowers. Proper timing and technique are essential to ensure the best possible quality and potency of the final product.
Determining Harvest Time
The optimal time to harvest cannabis depends on the desired effect and cannabinoid profile. For a more energizing and cerebral experience, it's best to harvest slightly earlier, when the pistils (hairs) are still mostly white. For a more sedative and relaxing effect, allowing the pistils to turn amber or brown before harvesting can result in a higher concentration of cannabinoids like CBD.
Harvesting and Drying
Harvesting involves carefully cutting down the entire plant or individual branches, depending on the desired yield and quality. The harvested buds should then be dried slowly and evenly to preserve their terpenes and cannabinoids. Drying should take place in a dark, well-ventilated area with a humidity level of around 50%. The drying process can take anywhere from a few days to a week, depending on the environmental conditions and the size of the buds.
Curing Cannabis
Curing is the final step in the post-harvest process, and it plays a crucial role in developing the cannabis's flavor, aroma, and smoothness. The curing process involves slowly reducing the moisture content of the buds over several weeks or months. There are various curing methods, including the air-curing method, which involves hanging the buds in a dark, well-ventilated area, and the jar-curing method, which involves storing the buds in airtight containers and periodically "burping" them to release built-up gases.
Future Implications and Legal Considerations

The legalization and regulation of cannabis cultivation vary widely across different regions and countries. It's essential to be aware of the local laws and regulations regarding cannabis cultivation, possession, and distribution. In many places, cultivation is legal for medicinal or recreational purposes, but it may be subject to specific guidelines and licensing requirements. Additionally, the environmental impact of cannabis cultivation, particularly in terms of energy consumption and water usage, is an important consideration for the industry's future sustainability.
What are some common challenges in growing cannabis, and how can they be overcome?
+Growing cannabis can present several challenges, including nutrient deficiencies, pests and diseases, and environmental stressors. To overcome these challenges, it’s essential to regularly monitor the plants’ health, provide proper nutrition and pest control measures, and maintain optimal environmental conditions. Additionally, staying informed about the latest cultivation techniques and technologies can help cultivators stay ahead of potential issues and maximize their yields.
How can I ensure the quality and potency of my cannabis harvest?
+Ensuring quality and potency starts with selecting high-quality seeds or clones and providing optimal growing conditions. Proper nutrient management, training, and pruning techniques can also significantly impact the final product’s quality. Finally, careful attention to the harvesting and curing process is crucial to preserve and enhance the cannabis’s desirable traits, such as flavor, aroma, and cannabinoid content.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when growing cannabis?
+Some common mistakes to avoid include overwatering, over-fertilizing, and providing inadequate light or ventilation. Additionally, neglecting pest and disease control can lead to significant losses in yield and quality. It’s also important to avoid over-pruning or topping the plants, as this can stress them and reduce overall growth and yield.