Why Do I Need A Firewall? Understanding Network Protection
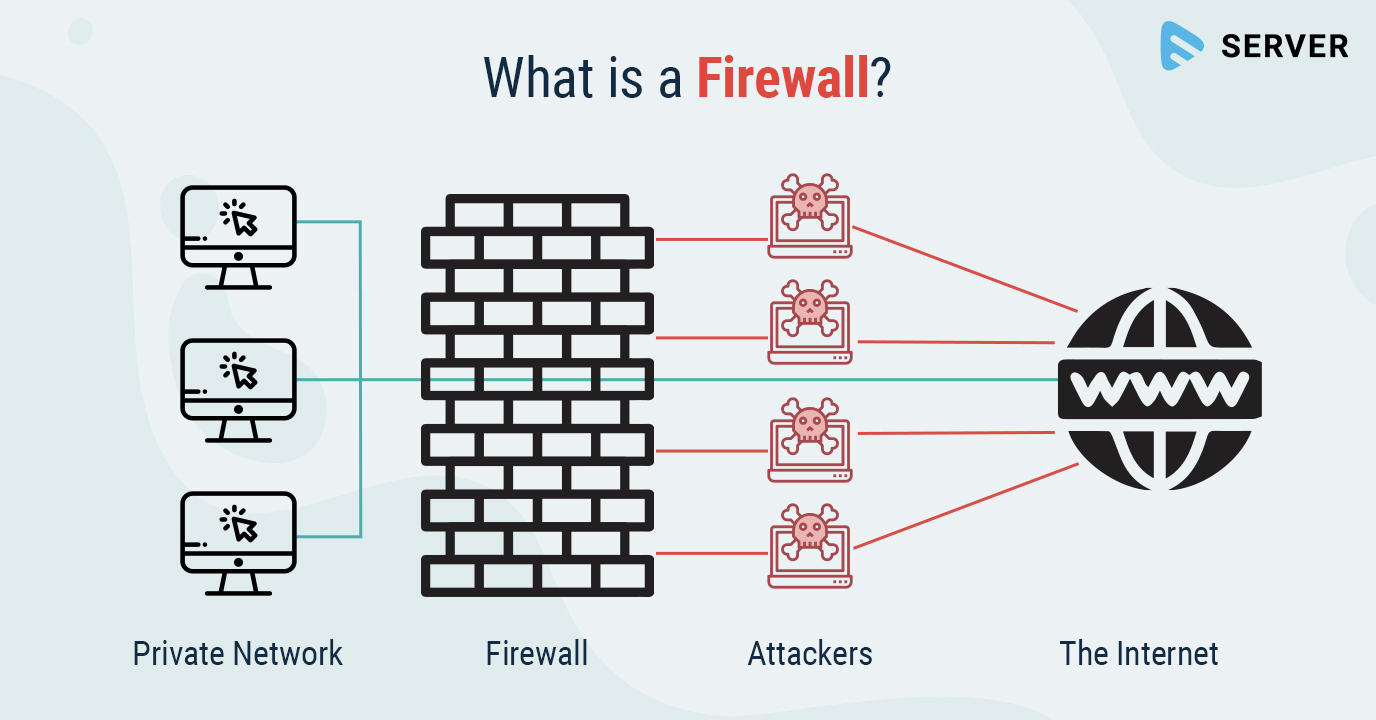
In today's interconnected digital landscape, network security has become an absolute necessity for individuals, businesses, and organizations alike. With the ever-increasing threat landscape and the constant evolution of cyberattacks, having robust network protection is crucial to safeguarding your digital assets and maintaining a secure online presence. This is where firewalls come into play, acting as the first line of defense against potential threats and unauthorized access.
A firewall is a security system designed to protect your network and its connected devices by monitoring and controlling the incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. It acts as a barrier between your trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, such as the internet, preventing unauthorized access and potential threats from reaching your sensitive data and systems.
The Role of Firewalls in Network Protection

Firewalls play a vital role in network protection by providing a comprehensive set of security measures. Here's a closer look at their key functions and benefits:
1. Filtering and Inspecting Network Traffic
Firewalls act as a gatekeeper, inspecting all incoming and outgoing network traffic. They use a set of predefined rules, known as access control lists (ACLs), to determine whether a packet of data should be allowed to pass through or be blocked. These rules are based on various criteria, including the source and destination IP addresses, port numbers, and protocols.
By filtering and inspecting network traffic, firewalls can identify and block potential threats, such as malicious packets, unauthorized access attempts, and known attack patterns. This helps prevent the spread of malware, ransomware, and other forms of cyberattacks.
2. Protection Against Unauthorized Access
One of the primary objectives of a firewall is to prevent unauthorized access to your network. It acts as a barrier, ensuring that only authorized users and devices can connect to your network resources. By implementing access control policies and authentication mechanisms, firewalls ensure that only trusted entities can access sensitive data and systems.
Firewalls can also enforce user-based access control, allowing administrators to define specific permissions for different users or user groups. This ensures that each user has the appropriate level of access required to perform their tasks, minimizing the risk of unauthorized data breaches.
3. Defense Against Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
DDoS attacks are a significant threat to network availability and performance. These attacks aim to overwhelm a network or server with a massive volume of traffic, rendering it inaccessible to legitimate users. Firewalls play a crucial role in mitigating DDoS attacks by identifying and blocking excessive or suspicious network traffic.
Advanced firewalls employ sophisticated algorithms and machine learning techniques to detect and mitigate DDoS attacks in real-time. They can identify patterns and anomalies in network traffic, allowing them to quickly identify and block malicious traffic, thus ensuring the availability and performance of your network infrastructure.
4. Application-Level Security
In addition to network-level protection, firewalls can also provide application-level security. They can inspect and analyze the content of network packets, allowing them to identify and block specific applications or services that may pose a security risk.
For example, firewalls can block access to known malicious websites, prevent the execution of unauthorized applications, and restrict the use of certain protocols that may be vulnerable to attacks. This level of application-specific security adds an extra layer of protection to your network, ensuring that only trusted and authorized applications can run.
5. Virtual Private Network (VPN) Support
Firewalls often include built-in support for Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), which allow remote users and branch offices to securely access the corporate network. VPNs create an encrypted tunnel between the remote user and the network, ensuring that data transmitted over the internet remains secure and private.
By integrating VPN functionality, firewalls provide a secure and reliable remote access solution, enabling employees to work remotely while maintaining the same level of network protection as if they were physically present in the office. This is especially crucial for businesses with a distributed workforce or those requiring remote access to sensitive data.
Types of Firewalls and Their Features

Firewalls come in various types, each with its own unique features and capabilities. Understanding the different types of firewalls can help you choose the most suitable solution for your network protection needs.
1. Packet-Filtering Firewalls
Packet-filtering firewalls are the most basic type of firewall. They operate at the network layer of the OSI model and examine the headers of each network packet to determine whether it should be allowed through or blocked. These firewalls use ACLs to define the rules for filtering incoming and outgoing traffic based on IP addresses, port numbers, and protocols.
While packet-filtering firewalls are simple and efficient, they have limitations in terms of security. They cannot inspect the content of network packets, making them vulnerable to certain types of attacks, such as IP spoofing and man-in-the-middle attacks. However, they are still widely used in smaller networks or as a basic security measure in conjunction with other firewall types.
2. Stateful Inspection Firewalls
Stateful inspection firewalls, also known as dynamic packet filtering firewalls, offer a more advanced level of security. They operate at the transport layer of the OSI model and maintain a state table that tracks the state of each network connection. This allows them to inspect not only the headers of network packets but also the data within the packets.
Stateful inspection firewalls can identify and block malicious packets based on their content, such as malicious code or unauthorized commands. They can also enforce connection-specific rules, ensuring that only legitimate and authorized connections are allowed to proceed. This makes them more effective in preventing various types of attacks, including intrusion attempts and unauthorized access.
3. Application-Level Gateways (Proxy Firewalls)
Application-level gateways, also known as proxy firewalls, operate at the application layer of the OSI model. They act as intermediaries between the internal network and external networks, intercepting and inspecting all network traffic. Proxy firewalls can perform deep packet inspection, analyzing the content of network packets to identify and block potential threats.
By acting as a proxy, these firewalls can provide additional security measures, such as hiding the internal network's IP addresses, preventing direct communication between internal and external networks. They can also enforce application-specific security policies, ensuring that only authorized applications and services are allowed to communicate.
4. Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs)
Next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) are the most advanced and comprehensive firewall solutions available. They combine the capabilities of traditional firewalls with additional security features, such as intrusion prevention systems (IPS), antivirus, and application control.
NGFWs offer a wide range of security functions, including deep packet inspection, application-level filtering, user-based access control, and threat intelligence. They can identify and block advanced threats, such as zero-day attacks and advanced persistent threats (APTs), by analyzing both the network and application layers.
NGFWs also provide centralized management and reporting, allowing network administrators to monitor and control the entire network infrastructure from a single console. This simplifies network management and ensures consistent security policies across the organization.
Benefits of Implementing a Firewall

Implementing a firewall offers numerous benefits for network protection and overall security. Here are some key advantages of having a firewall in place:
1. Enhanced Security
Firewalls provide an additional layer of security to your network, acting as a barrier against potential threats. By filtering and inspecting network traffic, they can identify and block malicious activities, unauthorized access attempts, and known attack patterns. This helps prevent data breaches, malware infections, and other security incidents.
2. Protection Against Zero-Day Attacks
Zero-day attacks refer to exploits or vulnerabilities that are unknown to the public and for which no official patches or fixes are available. These attacks can be highly dangerous as they exploit unpatched vulnerabilities, leaving systems vulnerable. Firewalls, especially NGFWs, can help mitigate the risk of zero-day attacks by employing advanced threat detection techniques and signature-based protection.
3. Network Segmentation
Firewalls enable network segmentation, which involves dividing a network into smaller, isolated segments. By implementing firewalls between different network segments, administrators can control the flow of traffic and restrict access between them. This helps contain potential threats within a specific segment, preventing them from spreading to the entire network.
4. Improved Network Performance
Firewalls can help optimize network performance by filtering and prioritizing network traffic. They can identify and block unnecessary or excessive traffic, such as spam emails or unsolicited network requests, reducing the load on the network infrastructure. This ensures that critical network resources are allocated efficiently, improving overall network performance and responsiveness.
5. Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Many industries and organizations are subject to various compliance and regulatory requirements, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). Firewalls play a crucial role in meeting these requirements by providing a secure network infrastructure and enforcing access control policies.
By implementing firewalls and ensuring proper configuration and management, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to data security and privacy, reducing the risk of non-compliance and potential legal consequences.
Best Practices for Firewall Implementation and Management

To maximize the effectiveness of your firewall and ensure optimal network protection, it is essential to follow best practices for implementation and management. Here are some key considerations:
1. Proper Configuration and Rule Management
Firewalls are only as effective as their configuration and rule management. It is crucial to define clear and precise rules that align with your organization's security policies and network architecture. Regularly review and update these rules to adapt to changing network requirements and emerging threats.
2. Centralized Management and Monitoring
Implementing a centralized management system for your firewall allows for efficient monitoring, configuration, and reporting. This ensures that network administrators can quickly identify and respond to security incidents, as well as make informed decisions regarding firewall rule changes and policy updates.
3. Regular Security Audits and Updates
Conducting regular security audits and keeping your firewall software up to date is essential for maintaining a strong security posture. Security audits help identify potential vulnerabilities and configuration issues, allowing you to take proactive measures to mitigate risks. Regular software updates ensure that your firewall has the latest security patches and features, keeping it effective against emerging threats.
4. User Awareness and Training
While firewalls provide robust network protection, user awareness and training are equally important. Educate your users about potential security risks, safe browsing practices, and the importance of following security policies. By fostering a security-conscious culture, you can reduce the likelihood of human error and potential security breaches.
5. Continuous Monitoring and Threat Intelligence
Firewalls should be continuously monitored to detect and respond to potential threats in real-time. Implement threat intelligence feeds and security information and event management (SIEM) solutions to stay informed about the latest threats and vulnerabilities. This allows you to proactively update your firewall rules and security policies to mitigate emerging risks.
Conclusion

Firewalls are an essential component of network protection, providing a robust defense against various cyber threats. By filtering and inspecting network traffic, enforcing access control policies, and offering advanced security features, firewalls help safeguard your digital assets and maintain the integrity of your network infrastructure.
Whether you choose a basic packet-filtering firewall or an advanced NGFW, proper implementation, configuration, and management are crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of your firewall. By following best practices and staying vigilant, you can ensure a secure and resilient network environment, protecting your organization from potential security breaches and cyberattacks.
How do I choose the right firewall for my network?
+When selecting a firewall, consider your network’s size, complexity, and specific security requirements. Evaluate the features and capabilities of different firewall types, such as packet-filtering, stateful inspection, proxy, and NGFWs. Assess your budget, as more advanced firewalls may require higher investments. Additionally, seek recommendations from IT professionals or security experts to make an informed decision.
Can firewalls protect against all types of cyberattacks?
+While firewalls provide a strong layer of protection, they cannot guarantee absolute security against all cyberattacks. Advanced threats, such as zero-day exploits and social engineering attacks, may still pose a risk. However, by combining firewalls with other security measures like antivirus software, intrusion prevention systems, and user awareness training, you can significantly reduce the likelihood and impact of cyberattacks.
What are some common challenges in firewall management?
+Common challenges in firewall management include keeping up with changing network requirements, maintaining a balance between security and network performance, and managing a large number of firewall rules. Regular security audits, proper documentation, and centralized management tools can help overcome these challenges and ensure effective firewall management.



