Syslog Port Setup: A Stepbystep Guide For Reliable Logging
Syslog is a widely used protocol for system logging and message logging, enabling efficient data collection and analysis from various devices and applications. Setting up Syslog ports correctly is crucial for ensuring reliable and secure logging. This step-by-step guide will walk you through the process of configuring Syslog ports, covering essential considerations and best practices to guarantee optimal performance and security.
Understanding Syslog Ports
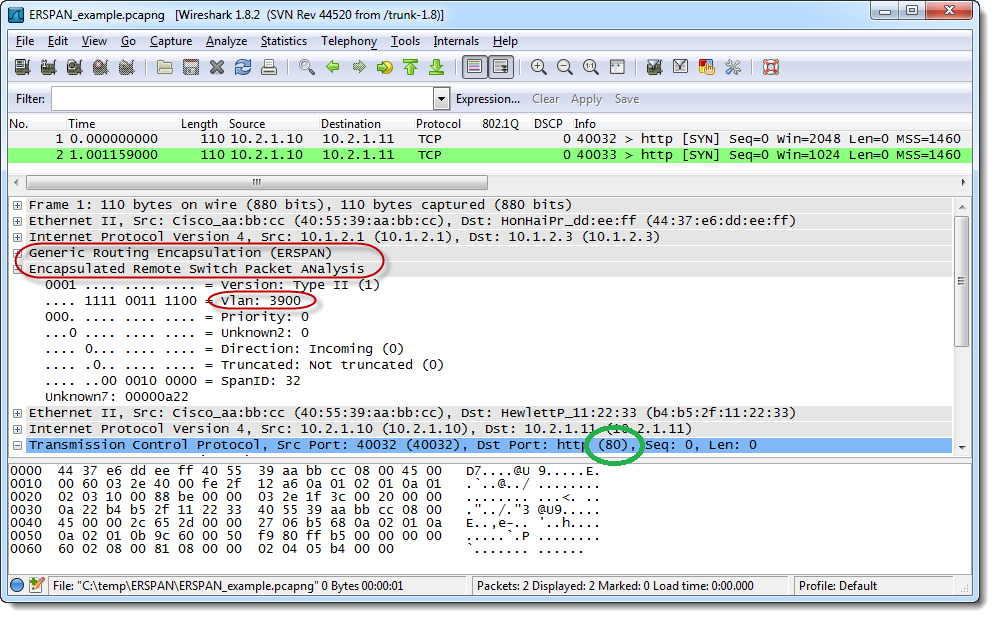
Syslog ports are designated communication channels used to transmit log messages between devices and Syslog servers. These ports play a vital role in ensuring the integrity and security of log data. By default, Syslog uses port 514 for both UDP (User Datagram Protocol) and TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) communication. However, it’s essential to understand that the default port may not always be the most secure or efficient choice for your specific environment.
Step 1: Assess Your Logging Requirements

Before configuring Syslog ports, it’s crucial to evaluate your logging requirements. Consider the following factors:
- The volume of log data generated by your devices and applications.
- The frequency of log message transmission.
- The level of security and privacy required for your log data.
- The network infrastructure and potential bottlenecks.
- The need for real-time logging or batch processing.
Analyzing Log Volume and Frequency
Understanding the volume and frequency of log data is essential. High-traffic environments with a large number of devices may require a different port configuration than low-traffic setups. Optimizing port settings can help distribute the load and prevent potential network congestion.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Syslog ports should be secured to protect sensitive log data from unauthorized access. Implementing encryption and authentication mechanisms is crucial to ensure data integrity and confidentiality. Consider using secure protocols like TLS (Transport Layer Security) or SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) to encrypt log transmissions.
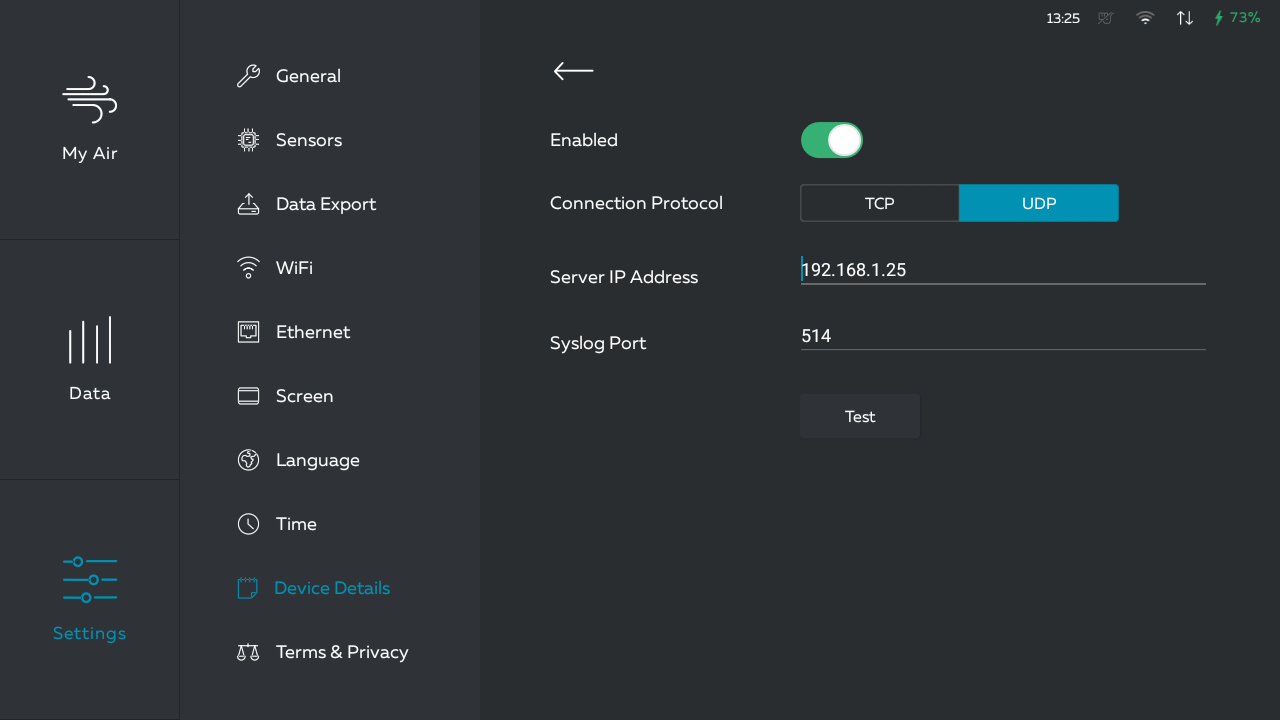
Step 2: Choose the Right Syslog Port

Selecting the appropriate Syslog port is a critical decision that can impact the performance and security of your logging infrastructure. Here are some considerations to guide your choice:
- Use the default port (514) only if your environment is relatively simple and secure.
- For high-security environments, consider using a non-standard port to reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
- Evaluate the compatibility of your Syslog server and client software with the chosen port.
- Ensure that the selected port is not already in use by other applications or services.
Example: Securing Syslog with a Non-Standard Port
In a highly secure environment, it may be beneficial to use a non-standard port for Syslog communication. For instance, instead of the default port 514, you could choose port 6514. This reduces the likelihood of unauthorized access attempts and potential security breaches.
Step 3: Configure Syslog Clients and Servers
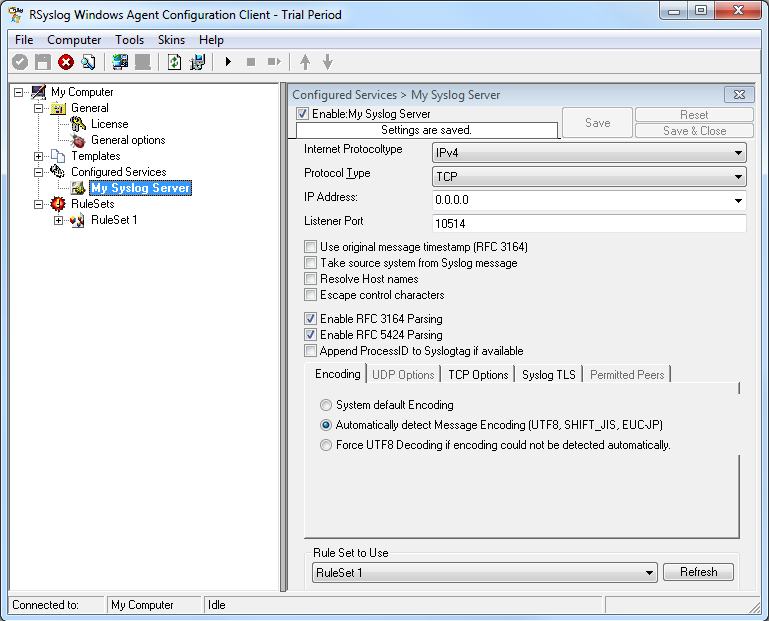
Once you’ve selected the appropriate Syslog port, it’s time to configure both the Syslog clients (devices generating log messages) and the Syslog server (the destination for log data). Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- On the Syslog server, open the configuration file and locate the port settings.
- Change the port number to the desired value, ensuring it matches the port configured on the clients.
- Save the configuration file and restart the Syslog server to apply the changes.
- On the Syslog clients, open the configuration settings and locate the Syslog server information.
- Update the port number to match the one configured on the server.
- Save the client configuration and restart the logging service to apply the new settings.
Best Practice: Test and Verify Configuration
After configuring the Syslog clients and server, it’s crucial to test the setup to ensure proper functionality. Use a Syslog testing tool or generate log messages to verify that the data is being transmitted correctly and securely. Monitor the logs for any errors or issues that may arise during the initial testing phase.
Step 4: Implement Security Measures

Securing your Syslog infrastructure is essential to protect sensitive log data. Here are some recommended security measures:
- Encrypt log transmissions using TLS or SSL to prevent data interception.
- Implement authentication mechanisms to ensure only authorized devices can send and receive log messages.
- Regularly update and patch your Syslog server and client software to address security vulnerabilities.
- Monitor your network for any suspicious activity or unauthorized access attempts.
Example: Implementing TLS Encryption
To enhance the security of your Syslog communication, you can configure your Syslog server and clients to use TLS encryption. This ensures that log data is encrypted during transmission, protecting it from potential eavesdroppers. Most modern Syslog implementations support TLS encryption, making it a straightforward process to enable this feature.
Step 5: Monitor and Optimize Performance

Even after initial setup, it’s essential to monitor the performance of your Syslog infrastructure regularly. Here are some key performance indicators to track:
- Log message transmission latency.
- Network bandwidth utilization.
- Syslog server and client resource usage.
- Log data storage and retention.
Performance Optimization Techniques
To optimize performance, consider the following techniques:
- Implement log message compression to reduce network bandwidth usage.
- Use log aggregation tools to centralize and analyze log data efficiently.
- Regularly review and adjust log retention policies to manage storage requirements.
- Consider load balancing or clustering Syslog servers for high-traffic environments.
Step 6: Ensure Redundancy and Failover

To maintain reliable logging, it’s crucial to implement redundancy and failover mechanisms. Here’s how you can achieve this:
- Set up multiple Syslog servers in a cluster or distributed architecture.
- Configure Syslog clients to send log messages to multiple servers for redundancy.
- Implement load balancing to distribute log messages across servers.
- Use heartbeat mechanisms to detect server failures and automatically switch to backup servers.
Benefits of Redundancy and Failover
By implementing redundancy and failover, you ensure that log data is always available and that logging operations continue seamlessly even in the event of server failures or network outages. This is especially critical in mission-critical environments where uninterrupted logging is essential for troubleshooting and incident response.
Step 7: Regularly Review and Update Configuration

Syslog port configuration is not a one-time task. It’s essential to regularly review and update your setup to adapt to changing requirements and emerging security threats. Here’s what you should consider:
- Monitor your network for any changes in traffic patterns or device deployments.
- Keep an eye on security advisories and patches for your Syslog software.
- Regularly assess the effectiveness of your security measures and encryption protocols.
- Update your configuration to align with best practices and industry standards.
Continuous Improvement through Configuration Reviews
By conducting regular configuration reviews, you can identify potential issues and inefficiencies in your Syslog setup. This proactive approach allows you to optimize performance, enhance security, and stay ahead of potential threats. It’s an essential practice to ensure that your logging infrastructure remains reliable, secure, and adaptable to changing business needs.
What are the potential risks of using the default Syslog port (514)?
+Using the default Syslog port (514) can increase the risk of unauthorized access and potential security breaches. Since this port is well-known, it may be a target for attackers. By changing to a non-standard port, you can reduce the likelihood of such attempts.
How often should I review and update my Syslog port configuration?
+It’s recommended to review your Syslog port configuration at least annually or whenever significant changes occur in your network infrastructure or security policies. Regular reviews ensure that your logging setup remains aligned with your evolving requirements and security best practices.
Can I use different ports for UDP and TCP Syslog communication?
+Yes, you can use different ports for UDP and TCP Syslog communication. This can be beneficial in certain scenarios, such as when you want to dedicate specific ports for different protocols or when you need to fine-tune your network configuration for optimal performance.