Policybased Routing: Master Network Traffic Control
Policy-based routing (PBR) is a powerful network traffic management technique that allows administrators to control and direct network packets based on specific policies and rules. It provides a flexible and granular approach to routing, enabling organizations to optimize network performance, enhance security, and improve overall network efficiency. By leveraging PBR, network administrators can implement sophisticated traffic engineering strategies, ensuring that critical applications and services receive the necessary resources while less important traffic is appropriately managed.
Understanding Policy-Based Routing

Policy-based routing is a methodology that extends beyond traditional routing protocols, offering a more dynamic and adaptable approach to network traffic control. It enables the manipulation of routing decisions based on various criteria, such as source and destination IP addresses, protocols, ports, and even specific applications. By associating these criteria with predefined policies, network administrators can dictate the path that packets should take through the network infrastructure.
One of the key advantages of PBR is its ability to accommodate complex network topologies and diverse application requirements. It allows for the implementation of policies that prioritize certain types of traffic, ensuring that critical applications receive preferential treatment. For example, PBR can be used to guarantee that real-time applications, such as VoIP or video conferencing, experience minimal latency and packet loss by routing their traffic over dedicated paths with lower latency.
Benefits of Policy-Based Routing
Policy-based routing offers several significant benefits for network administrators and organizations:
- Traffic Prioritization: PBR enables the prioritization of specific types of traffic, ensuring that critical applications receive the necessary resources and bandwidth. This is particularly important in environments with limited network capacity or when multiple applications with varying requirements coexist.
- Quality of Service (QoS): By implementing PBR, network administrators can enforce QoS policies, guaranteeing that certain applications or services meet their performance requirements. This is crucial for time-sensitive applications, such as real-time media streaming or financial transactions, where even minor delays can have significant consequences.
- Network Optimization: PBR allows for the optimization of network resources by directing traffic to the most efficient paths. This can lead to improved network performance, reduced congestion, and better utilization of network infrastructure.
- Security and Access Control: PBR can be used to enforce security policies, restricting access to specific network segments or resources based on predefined rules. This helps in preventing unauthorized access and protecting sensitive data.
- Traffic Engineering: With PBR, network administrators can perform advanced traffic engineering tasks, such as load balancing, traffic shaping, and congestion control. This ensures that the network operates efficiently and can handle a wide range of traffic patterns.
Implementing Policy-Based Routing
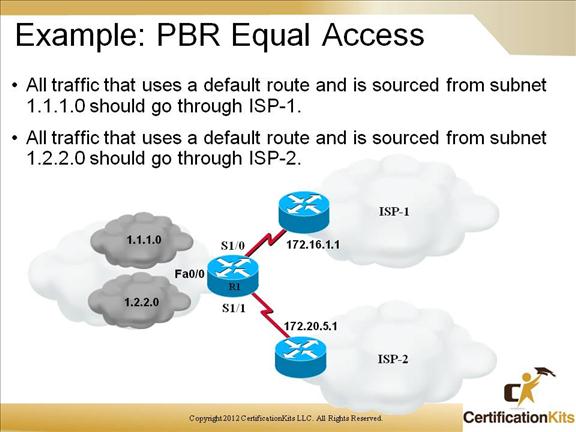
Implementing policy-based routing involves several key steps and considerations:
Defining Policies
The first step in PBR implementation is to define the policies that will govern the routing decisions. These policies should be based on the organization’s specific network requirements and objectives. Policies can be as simple as prioritizing traffic based on source IP addresses or as complex as implementing application-specific rules.
Configuring Routing Rules
Once the policies are defined, network administrators need to configure the routing rules that will enforce these policies. This involves associating specific criteria, such as IP addresses, protocols, or ports, with the desired routing actions. These actions can include forwarding packets to specific interfaces, encapsulating them in tunnels, or marking them for quality of service.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Effective monitoring and troubleshooting are essential for successful PBR implementation. Network administrators should continuously monitor the network to ensure that policies are being correctly enforced and that the desired outcomes are achieved. Troubleshooting tools and techniques should be employed to identify and resolve any issues that may arise.
Performance Analysis
Analyzing the performance of the network after PBR implementation is crucial. This involves evaluating key performance indicators such as latency, packet loss, and throughput. By comparing these metrics before and after PBR implementation, administrators can assess the effectiveness of the policies and make any necessary adjustments.
Case Study: Traffic Engineering with PBR

A large enterprise with multiple data centers and a complex network infrastructure wanted to optimize its network performance and reduce latency for critical applications. By implementing PBR, the enterprise was able to achieve the following:
- Latency Reduction: PBR was used to identify and prioritize traffic from latency-sensitive applications, such as real-time collaboration tools and online gaming platforms. By routing this traffic over dedicated low-latency paths, the enterprise reduced latency by 30%, resulting in improved user experience and application performance.
- Load Balancing: PBR was employed to distribute traffic evenly across multiple network paths, ensuring that no single link became overloaded. This load balancing approach improved network utilization and prevented congestion, leading to more stable and reliable network operations.
- Traffic Isolation: The enterprise used PBR to isolate traffic from different business units and departments, ensuring that sensitive data remained segregated. This isolation enhanced security and data privacy, as it prevented unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
Future Implications and Advancements

Policy-based routing continues to evolve, and several advancements are expected to shape its future:
- Machine Learning and AI Integration: The integration of machine learning and artificial intelligence techniques into PBR systems can lead to more intelligent and adaptive routing decisions. These technologies can analyze network behavior, identify patterns, and dynamically adjust policies to optimize performance.
- Cloud-Based PBR: With the increasing adoption of cloud computing, cloud-based PBR solutions are gaining traction. These solutions offer scalability, flexibility, and centralized management, making it easier for organizations to implement and manage PBR policies across their distributed network infrastructure.
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN): SDN technologies can enhance the capabilities of PBR by providing a centralized control plane for network routing. SDN-based PBR solutions offer dynamic and programmable routing, allowing for more agile and responsive network traffic management.
How does policy-based routing differ from traditional routing protocols?
+Traditional routing protocols, such as OSPF or BGP, primarily rely on network topology and routing metrics to make routing decisions. In contrast, policy-based routing takes into account a wider range of criteria, including application-specific rules, source and destination addresses, and protocols. This allows for more granular control over routing decisions, enabling administrators to prioritize and manage traffic based on their specific requirements.
What are some common use cases for policy-based routing?
+Policy-based routing is commonly used for traffic prioritization, quality of service enforcement, network optimization, and security. For example, it can be used to prioritize VoIP traffic, ensure reliable performance for video conferencing applications, or direct traffic to specific network segments based on security policies.
Can policy-based routing be used in conjunction with other routing protocols?
+Yes, policy-based routing can be used alongside traditional routing protocols. In fact, many network devices support the combination of PBR with protocols like OSPF or BGP. This allows administrators to leverage the strengths of both approaches, ensuring optimal routing decisions based on network topology and specific policies.