Online Certificate Status Protocol
The Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) is a critical component of modern digital security infrastructure, playing a pivotal role in the validation and verification of digital certificates. As the internet continues to evolve and the reliance on secure online transactions increases, OCSP has become an indispensable tool for ensuring the integrity and authenticity of digital communications.
The Evolution of OCSP: A Brief Overview
OCSP emerged as a response to the limitations of its predecessor, the Certificate Revocation List (CRL) system. While CRLs provided a means to check the revocation status of digital certificates, they suffered from scalability and efficiency issues, particularly as the number of certificates and their revocations grew. OCSP was designed to address these shortcomings, offering a more efficient and dynamic approach to certificate status verification.
Developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and first published in 1999, OCSP has since become a cornerstone of digital security protocols. Its ability to provide real-time, up-to-date information about the status of digital certificates has made it an essential tool for maintaining the security and integrity of online transactions.
How OCSP Works: A Technical Deep Dive

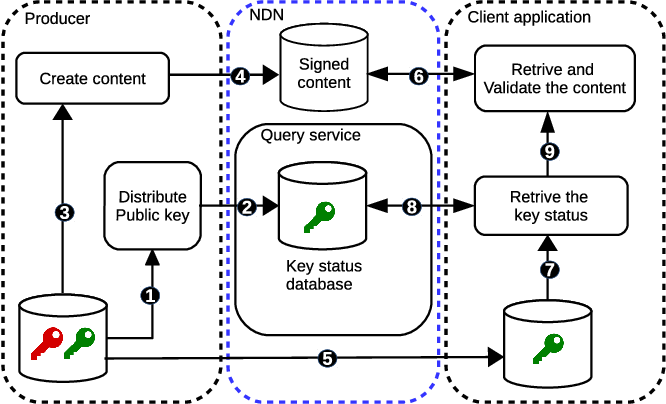
At its core, OCSP operates as a request-response protocol. When a client, such as a web browser, needs to verify the validity of a digital certificate, it sends an OCSP request to an OCSP responder, which is typically a server operated by a Certificate Authority (CA) or a trusted third party.
The OCSP Request
An OCSP request contains the following key elements:
- Version: This specifies the OCSP protocol version being used.
- Requester: The entity making the request, often identified by its certificate serial number.
- Certificate Serial Number: The unique identifier of the certificate whose status is being queried.
- Nonce: A random number used to prevent replay attacks.
- Optional Extensions: Additional information or requests, such as a list of certificate serial numbers to be checked.
The request is typically signed by the requester's certificate to ensure its authenticity and integrity.
The OCSP Response
Upon receiving a valid OCSP request, the responder generates a response, which includes the following:
- Version: The OCSP protocol version.
- Response Status: Indicates whether the response is successful, the certificate status is unknown, or if an error has occurred.
- Produced At: The timestamp indicating when the response was generated.
- Next Update: An optional field specifying the next time the responder plans to update the certificate status.
- Certificate Status: The actual status of the certificate, which can be good, revoked, unknown, or undetermined.
- Optional Extensions: Additional information or responses, such as a list of certificate serial numbers and their statuses.
Like the request, the response is also typically signed by the responder's certificate to ensure its authenticity and integrity.
OCSP in Practice: Real-World Applications
OCSP finds extensive use in various digital security contexts, particularly in the following areas:
Web Browser Certificate Validation
Web browsers, such as Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Microsoft Edge, use OCSP to verify the validity of SSL/TLS certificates presented by web servers. This ensures that users are connecting to legitimate, secure websites and not potential phishing or malware sites.
Email Security
OCSP is employed in email security protocols like S/MIME to verify the validity of digital signatures and certificates used in secure email communication. This helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information and ensures the integrity of the email ecosystem.
Network Security
In enterprise networks, OCSP is used to validate the certificates presented by clients and servers during authentication and authorization processes. This helps prevent unauthorized access to network resources and ensures the integrity of the network infrastructure.
IoT Device Security
With the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, OCSP plays a crucial role in ensuring the security of these devices. By verifying the validity of certificates used in IoT communications, OCSP helps prevent unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
Advantages and Challenges of OCSP

OCSP offers several advantages over traditional CRL systems, including real-time certificate status updates, reduced network bandwidth usage, and improved performance. However, it also presents certain challenges, such as the potential for single points of failure (if the OCSP responder is unavailable) and the need for frequent, timely updates to maintain certificate status accuracy.
Addressing OCSP Challenges
To mitigate these challenges, several best practices and solutions have emerged:
- OCSP Stapling: This technique allows the server to provide the OCSP response along with the certificate, reducing the need for clients to query the OCSP responder directly.
- OCSP Caching: By caching OCSP responses, clients can avoid frequent queries to the responder, improving performance and reducing network traffic.
- OCSP Must-Staple: This extension requires the server to staple the OCSP response to the certificate, ensuring that clients always receive the latest certificate status.
The Future of OCSP: Emerging Trends and Technologies
As digital security continues to evolve, OCSP is likely to remain a cornerstone of certificate status verification. However, emerging technologies and protocols, such as Certificate Transparency and DNS-based Authentication of Named Entities (DANE), may offer alternative or complementary approaches to certificate validation and revocation.
Additionally, the increasing adoption of zero-trust security models, which emphasize strict identity verification and least-privilege access, will likely drive further innovation and development in the field of digital certificate validation, including OCSP and its alternatives.
What is the difference between OCSP and CRL?
+OCSP and CRL are both protocols used for checking the revocation status of digital certificates. However, they differ in their approach and efficiency. OCSP provides real-time, dynamic certificate status updates, while CRLs are static lists that need to be frequently updated and can be resource-intensive to manage. OCSP is generally considered more efficient and scalable for modern digital security needs.
What are some common use cases for OCSP?
+OCSP is commonly used in web browser certificate validation, email security protocols, network security authentication, and IoT device security. It ensures that digital certificates presented by various entities are valid and have not been revoked, helping to maintain the integrity and security of digital communications and transactions.
How can OCSP challenges be mitigated?
+OCSP challenges, such as single points of failure and the need for frequent updates, can be mitigated through techniques like OCSP stapling, caching, and the OCSP Must-Staple extension. These measures help reduce the reliance on OCSP responders, improve performance, and ensure that clients always receive the latest certificate status information.



