Master Rdp Network Ports: A Comprehensive Security Guide

In today's interconnected world, remote desktop protocol (RDP) has become an essential tool for remote access and management of computer systems. However, with the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, ensuring the security of RDP network ports has become a critical concern for network administrators and security professionals. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the intricacies of RDP network ports, offering a detailed understanding of their functionality, potential vulnerabilities, and effective security measures to safeguard against unauthorized access and potential breaches.
Understanding RDP Network Ports
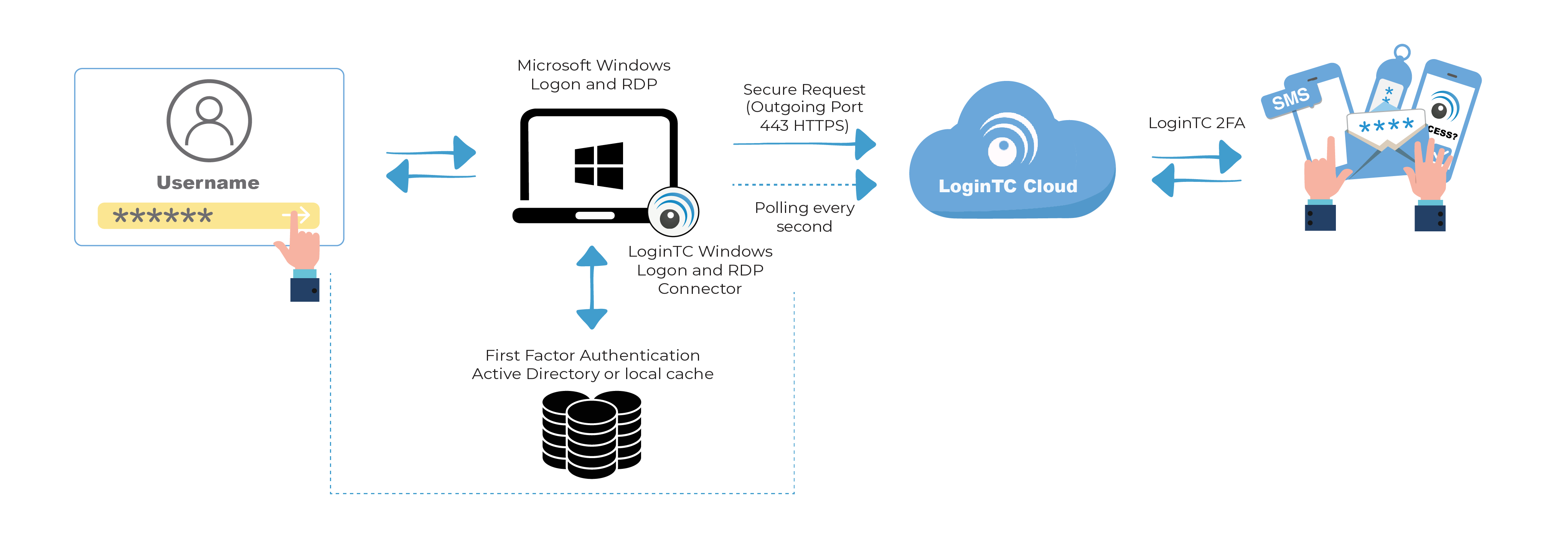
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a proprietary protocol developed by Microsoft, which allows users to connect to and control a remote computer over a network connection. At its core, RDP is designed to provide a secure and efficient way to access and manage remote systems, making it an indispensable tool for system administrators, IT professionals, and even remote workers.
The functionality of RDP relies on the use of specific network ports to establish and maintain connections. These ports act as virtual gateways, facilitating the exchange of data between the client and the server. By default, RDP uses TCP port 3389 for this purpose, making it a critical component in the overall RDP infrastructure.
However, the reliance on a single, well-known port can also present a potential security risk. Malicious actors are well aware of the default port assignments, and this knowledge can be exploited to launch targeted attacks. Additionally, the increasing popularity of RDP as a remote access solution has made it a prime target for cybercriminals, who employ various techniques to exploit vulnerabilities and gain unauthorized access to sensitive systems.
Common RDP Port Assignments
While TCP port 3389 is the standard for RDP, there are other ports that are commonly used for specific purposes within the RDP ecosystem. These include:
- TCP 3388: Often used as an alternative port for RDP connections, especially in environments where port 3389 is blocked or restricted.
- TCP 3390-3399: These ports are sometimes used for load balancing or to support multiple RDP connections simultaneously.
- UDP 3389: While RDP primarily uses TCP, some implementations may also utilize UDP for certain features or protocols.
It's important to note that the use of non-standard ports can provide an additional layer of security, as it makes it more difficult for attackers to identify and target RDP services. However, it's crucial to ensure that any port changes are properly configured and documented to avoid compatibility issues and potential disruptions to RDP connectivity.
RDP Port Security Challenges

The security of RDP network ports is a complex and multifaceted issue. While RDP itself incorporates various security measures, such as encryption and authentication, the nature of remote access inherently introduces new vulnerabilities and attack vectors. Here are some of the key challenges and risks associated with RDP port security:
Brute Force Attacks
Brute force attacks are a common threat to RDP port security. In this type of attack, an attacker systematically tries different username and password combinations to gain unauthorized access to a system. RDP’s default use of port 3389 makes it an attractive target for brute force attacks, as attackers can automate the process and rapidly attempt a large number of login attempts.
To mitigate the risk of brute force attacks, it's essential to implement strong password policies and consider using two-factor authentication (2FA) or multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security. Additionally, rate-limiting mechanisms can be employed to restrict the number of login attempts within a certain time frame, making it more difficult for attackers to succeed.
RDP Exploits and Vulnerabilities
RDP, like any software, is not immune to vulnerabilities and exploits. Over the years, various security flaws have been discovered in RDP implementations, ranging from buffer overflows to remote code execution vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access, execute malicious code, or even take control of the affected system.
To address these risks, it's crucial to keep RDP software up to date with the latest security patches and updates. Regularly applying security updates ensures that known vulnerabilities are mitigated, reducing the likelihood of successful attacks. Additionally, implementing network-level security measures, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS), can help detect and block potential RDP-based attacks.
Unsecured RDP Connections
Another significant security challenge is the use of unsecured RDP connections. By default, RDP connections are encrypted using the RDP protocol, which provides a reasonable level of security. However, if the encryption is not properly configured or if weak encryption algorithms are used, RDP connections can become vulnerable to interception and decryption by malicious actors.
To ensure secure RDP connections, it's essential to implement strong encryption protocols, such as TLS (Transport Layer Security) or SSL (Secure Sockets Layer). These protocols provide robust encryption and authentication mechanisms, making it significantly more difficult for attackers to intercept and exploit RDP traffic. Additionally, using VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) or IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) can further enhance the security of RDP connections by providing an additional layer of encryption and authentication.
Securing RDP Network Ports

Securing RDP network ports is a critical aspect of overall network security. By implementing a combination of technical and administrative controls, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and potential breaches. Here are some key strategies and best practices for securing RDP network ports:
Network Segmentation and Firewalls
Network segmentation involves dividing a larger network into smaller, more secure segments. By isolating RDP servers and clients into their own network segments, organizations can limit the potential impact of a successful attack. This approach ensures that even if an attacker gains access to one segment, they won’t have unrestricted access to the entire network.
Firewalls play a crucial role in network segmentation. By deploying firewalls at the perimeter of each network segment, organizations can control the flow of traffic and enforce access policies. Firewalls can be configured to allow RDP traffic only from trusted sources, such as specific IP addresses or subnets, further reducing the attack surface.
RDP Port Filtering and Access Control
Implementing port filtering and access control measures is essential for securing RDP network ports. By default, RDP listens on TCP port 3389, but this can be a target for attackers. To mitigate this risk, organizations can consider the following strategies:
- Port Blocking: Blocking incoming RDP traffic on port 3389 at the network perimeter can prevent unauthorized access attempts. However, this approach may also block legitimate RDP connections, so it's important to carefully consider the impact on business operations.
- Port Restriction: Instead of blocking the port entirely, organizations can restrict RDP access to specific IP addresses or subnets. This allows authorized users to connect while blocking unauthorized access attempts.
- Port Forwarding: In some cases, organizations may need to allow RDP connections from the internet. In such scenarios, port forwarding can be used to direct incoming RDP traffic to a specific server or subnet, providing an additional layer of control and security.
RDP Gateway and VPN Solutions
Implementing an RDP gateway or VPN (Virtual Private Network) solution can significantly enhance the security of RDP network ports. An RDP gateway acts as an intermediary between the client and the server, providing an additional layer of security and control. By authenticating and encrypting RDP traffic, gateways ensure that only authorized users can access the remote system.
VPNs, on the other hand, provide a secure and encrypted tunnel for all network traffic, including RDP. By establishing a VPN connection, organizations can ensure that RDP traffic is protected from interception and unauthorized access. Additionally, VPNs can be configured to allow access only from specific devices or locations, adding an extra layer of security.
Strong Authentication and Access Controls
Implementing strong authentication mechanisms is crucial for securing RDP network ports. While basic username and password authentication is a starting point, it’s not sufficient to prevent unauthorized access. Organizations should consider the following authentication and access control measures:
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide a second form of authentication, such as a one-time password (OTP) or a biometric factor, in addition to their username and password.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA takes 2FA a step further by requiring multiple forms of authentication. This could include a combination of something the user knows (e.g., a password), something the user has (e.g., a hardware token), and something the user is (e.g., a biometric factor).
- Certificate-Based Authentication: Certificate-based authentication uses digital certificates to authenticate users and devices. This approach provides a high level of security and can be used in conjunction with other authentication methods for added protection.
Monitoring and Incident Response

Effective monitoring and incident response are critical components of a robust RDP security strategy. By implementing proactive monitoring and response measures, organizations can quickly detect and respond to potential security incidents, minimizing the impact and preventing further damage.
Log Monitoring and Analysis
Monitoring and analyzing RDP logs is essential for detecting suspicious activities and potential security incidents. By examining RDP logs, security teams can identify patterns of unauthorized access attempts, unusual user behavior, or other indicators of potential threats. Here are some key aspects of log monitoring and analysis:
- Log Retention: Organizations should maintain a comprehensive log retention policy, ensuring that RDP logs are stored for an appropriate period of time. This allows for historical analysis and helps in identifying long-term trends and potential security threats.
- Log Aggregation and Correlation: Aggregating logs from multiple sources, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and RDP servers, can provide a more holistic view of network activity. Correlating logs can help identify potential security incidents and provide valuable context for incident response.
- Log Analysis Tools: Utilizing specialized log analysis tools can automate the process of identifying suspicious activities and potential security incidents. These tools can detect anomalies, flag unauthorized access attempts, and provide real-time alerts to security teams.
Network Traffic Analysis
Analyzing network traffic can provide valuable insights into potential RDP-related security incidents. By examining network traffic patterns, security teams can identify unusual or suspicious behavior, such as excessive RDP connection attempts, large data transfers, or anomalous traffic flows. Here are some key aspects of network traffic analysis:
- Traffic Monitoring: Deploying network monitoring tools, such as packet sniffers or network analyzers, can help capture and analyze network traffic in real time. This allows security teams to detect and respond to potential security incidents promptly.
- Protocol Analysis: Analyzing the protocols used in RDP traffic can provide valuable information about the nature of the connection. For example, examining the encryption protocol and key exchange mechanisms can help identify potential weaknesses or unauthorized access attempts.
- Traffic Anomaly Detection: Implementing machine learning algorithms and behavioral analysis techniques can help detect anomalous traffic patterns. By establishing a baseline of normal RDP traffic, security teams can identify deviations that may indicate potential security incidents.
Incident Response Planning
Developing a comprehensive incident response plan is crucial for effectively managing and mitigating RDP-related security incidents. An incident response plan outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a security breach, ensuring a coordinated and efficient response. Here are some key components of an effective incident response plan:
- Incident Identification: Establishing clear criteria for identifying a security incident is essential. This could include detecting unauthorized access attempts, identifying suspicious network traffic, or discovering signs of a successful breach.
- Incident Containment: Once an incident is identified, the first step is to contain the threat to prevent further damage. This may involve isolating affected systems, disabling RDP access, or implementing temporary security measures to prevent the spread of the incident.
- Incident Eradication: After containing the incident, the next step is to eradicate the threat. This could involve removing malicious software, patching vulnerabilities, or implementing additional security controls to prevent future incidents.
- Incident Recovery: Once the threat is eradicated, the focus shifts to recovering from the incident. This may involve restoring affected systems, data, and services to their pre-incident state. It's important to have a well-defined recovery plan to minimize downtime and ensure business continuity.
Future Trends and Recommendations

As the landscape of cyber threats continues to evolve, it’s essential for organizations to stay ahead of the curve and adapt their RDP security strategies accordingly. Here are some future trends and recommendations to consider:
Zero Trust Security Model
The Zero Trust security model is gaining traction as a more effective approach to network security. Unlike traditional security models that rely on a perimeter-based approach, Zero Trust assumes that no user or device can be trusted by default. This model requires continuous authentication, authorization, and monitoring of all users and devices, regardless of their location or network segment.
By adopting a Zero Trust security model, organizations can significantly enhance the security of their RDP network ports. This approach ensures that even if an attacker gains initial access, they will face additional layers of security controls, making it more difficult to exploit RDP vulnerabilities or move laterally within the network.
AI and Machine Learning for Threat Detection
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming the field of cybersecurity, and their potential in threat detection and response is immense. By leveraging AI and ML algorithms, organizations can analyze vast amounts of data in real time, identifying patterns and anomalies that may indicate potential security incidents.
Applying AI and ML to RDP security can help detect and respond to threats more efficiently. These technologies can analyze RDP logs, network traffic, and user behavior to identify suspicious activities, unauthorized access attempts, or potential vulnerabilities. By automating the threat detection process, organizations can enhance their security posture and respond to incidents more promptly.
Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Conducting regular security audits and penetration testing is crucial for identifying and addressing potential vulnerabilities in RDP network ports. Security audits involve a comprehensive review of the RDP infrastructure, including network configurations, access controls, and security policies. Penetration testing, on the other hand, simulates real-world attacks to identify weaknesses and assess the effectiveness of existing security measures.
By regularly conducting security audits and penetration testing, organizations can proactively identify and mitigate potential security risks. These exercises help organizations stay ahead of emerging threats and ensure that their RDP network ports are secure and resilient against a wide range of attack vectors.
What is the default port used by RDP?
+The default port used by RDP is TCP port 3389. This port is well-known and widely used for RDP connections.
How can I secure my RDP network ports?
+To secure your RDP network ports, consider implementing network segmentation, port filtering, strong authentication mechanisms, and monitoring tools. Additionally, keep your RDP software up to date with the latest security patches.
What are some common RDP security challenges?
+Common RDP security challenges include brute force attacks, RDP exploits and vulnerabilities, and unsecured RDP connections. These challenges can be mitigated through strong password policies, regular security updates, and robust encryption protocols.
How can I detect and respond to RDP-related security incidents?
+To detect and respond to RDP-related security incidents, implement log monitoring and analysis, network traffic analysis, and incident response planning. These measures help identify suspicious activities and provide a structured approach to managing security incidents.



