5 Vlan Tagging Techniques To Enhance Network Efficiency
In the realm of computer networking, Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) play a pivotal role in enhancing network efficiency and security. VLANs are logical groupings of devices that function as independent networks, allowing for better traffic management, security, and scalability. This article delves into five VLAN tagging techniques that are instrumental in optimizing network performance and ensuring efficient data transmission.
1. 802.1Q VLAN Tagging

The 802.1Q standard is one of the most widely used VLAN tagging methods in Ethernet networks. It involves the addition of a 4-byte tag to each Ethernet frame, containing information about the VLAN to which the frame belongs. This tag includes a 3-bit priority field (used for Quality of Service, or QoS) and a 12-bit VLAN ID field, allowing for up to 4,094 unique VLANs (IDs 0 and 4095 are reserved). The 802.1Q tag is inserted between the source MAC address and the EtherType/Length field in the Ethernet frame.
802.1Q Implementation
Implementing 802.1Q involves configuring network switches to tag and untag frames as they enter and exit VLANs. This process is transparent to end devices, as the switches handle the tagging and untagging. When a switch receives a frame, it examines the VLAN ID in the tag to determine the frame’s VLAN membership. If the frame is destined for a device in the same VLAN, the switch removes the tag before forwarding the frame. If the frame needs to be sent to a device in a different VLAN, the switch adds a new tag with the appropriate VLAN ID before forwarding.
Benefits of 802.1Q
- Enhanced Security: 802.1Q allows for the segregation of network traffic, preventing unauthorized access and improving overall network security.
- Improved Performance: By separating traffic into different VLANs, 802.1Q reduces network congestion and improves the efficiency of data transmission.
- Scalability: With support for up to 4,094 VLANs, 802.1Q enables the creation of large, complex network topologies.
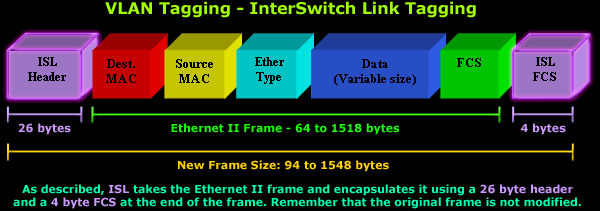
2. ISL (Inter-Switch Link) Tagging

ISL is a VLAN tagging protocol developed by Cisco for use in their switches. It was designed to overcome the limitations of the 802.1Q standard, particularly in large-scale networks. ISL encapsulates the entire Ethernet frame, including the original Ethernet header, within a new frame. This new frame includes a 26-byte header and a 4-byte trailer, which contain information about the VLAN and the original frame.
ISL Functionality
ISL operates by breaking down the original Ethernet frame into smaller fragments, each of which is encapsulated within an ISL frame. These fragments are then reassembled at the receiving end to recreate the original frame. ISL also supports VLAN trunking, which allows multiple VLANs to share a single link, thus conserving bandwidth and simplifying network management.
Advantages of ISL
- Compatibility: ISL is compatible with both Cisco and non-Cisco switches, making it a versatile tagging protocol.
- Enhanced Performance: By encapsulating the entire frame, ISL provides better performance in large-scale networks, especially when dealing with large frames.
- VLAN Trunking: ISL’s support for VLAN trunking simplifies network management by allowing multiple VLANs to share a single link.
3. Q-in-Q (802.1ad) VLAN Stacking

Q-in-Q, also known as 802.1ad, is a VLAN tagging technique that allows multiple VLANs to coexist on the same physical link. It is particularly useful in service provider networks, where service providers need to carry traffic from multiple customers over a single link.
Q-in-Q Operation
In Q-in-Q, an outer 802.1Q tag is added to the frame, which carries the service provider’s VLAN ID. This outer tag is then followed by the customer’s original frame, which may already have an inner 802.1Q tag with the customer’s VLAN ID. This allows the service provider to maintain separate VLANs for different customers, while still using a single physical link.
Q-in-Q Benefits
- Customer VLAN Preservation: Q-in-Q ensures that customer VLAN configurations remain intact, allowing service providers to offer VLAN-based services without altering customer networks.
- Efficient Resource Utilization: By allowing multiple VLANs on a single link, Q-in-Q optimizes resource utilization and reduces the need for additional links.
- Enhanced Security: Q-in-Q provides an extra layer of security by isolating customer traffic from each other and from the service provider’s network.
4. VLAN Double Tagging (802.1Q-in-Q)
VLAN Double Tagging, or 802.1Q-in-Q, is a variation of Q-in-Q that allows for the stacking of multiple 802.1Q tags within a single frame. This technique is particularly useful in environments where multiple VLANs need to be nested within each other, such as in cloud computing or virtualized environments.
802.1Q-in-Q Implementation
In 802.1Q-in-Q, an outer 802.1Q tag is added to the frame, which carries the service provider’s VLAN ID. This outer tag is then followed by an inner 802.1Q tag, which carries the customer’s VLAN ID. This allows for the creation of nested VLANs, where a single frame can belong to multiple VLANs simultaneously.
Advantages of 802.1Q-in-Q
- Flexibility: 802.1Q-in-Q provides the flexibility to create complex VLAN topologies, especially in virtualized environments where multiple VLANs need to coexist on a single link.
- Enhanced Security: By nesting VLANs, 802.1Q-in-Q adds an extra layer of security, as it allows for the segregation of traffic at multiple levels.
- Efficient Resource Utilization: Like Q-in-Q, 802.1Q-in-Q optimizes resource utilization by allowing multiple VLANs to share a single link.
5. VLAN Translation (802.1Q Translation)
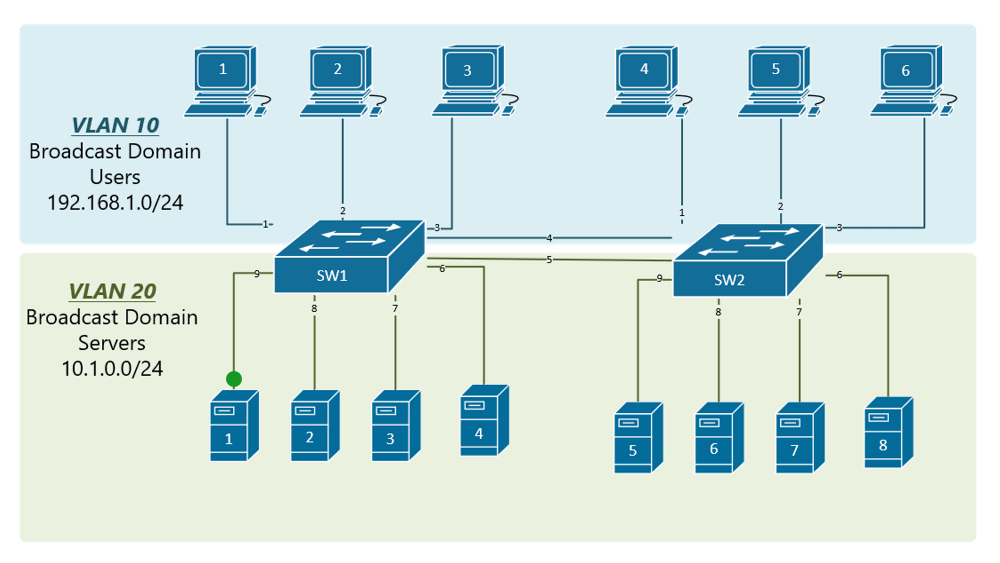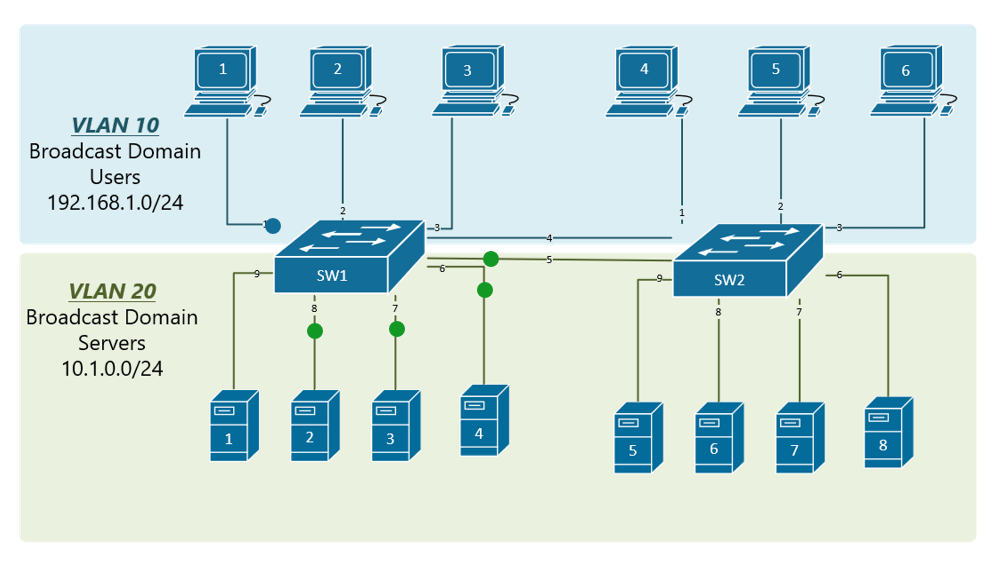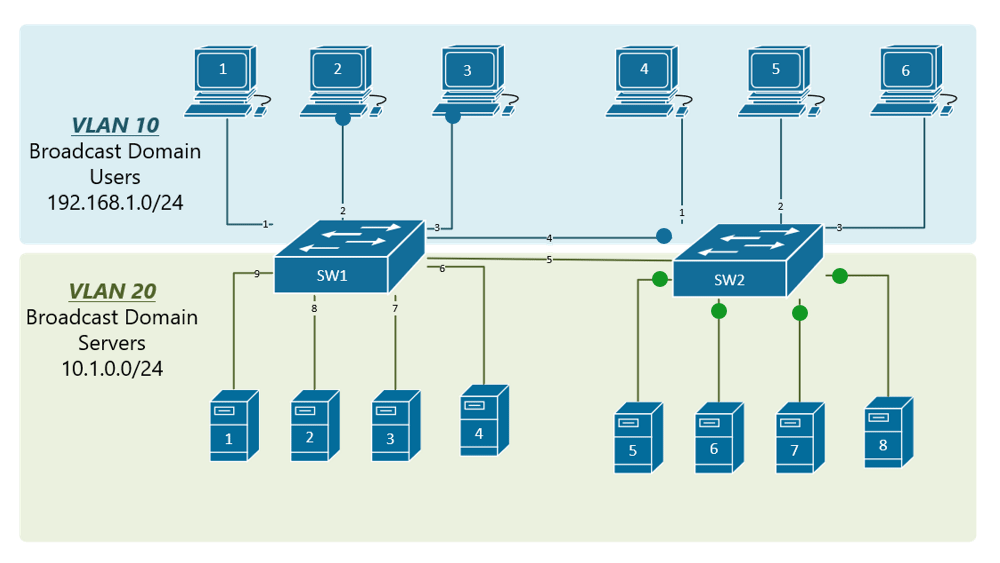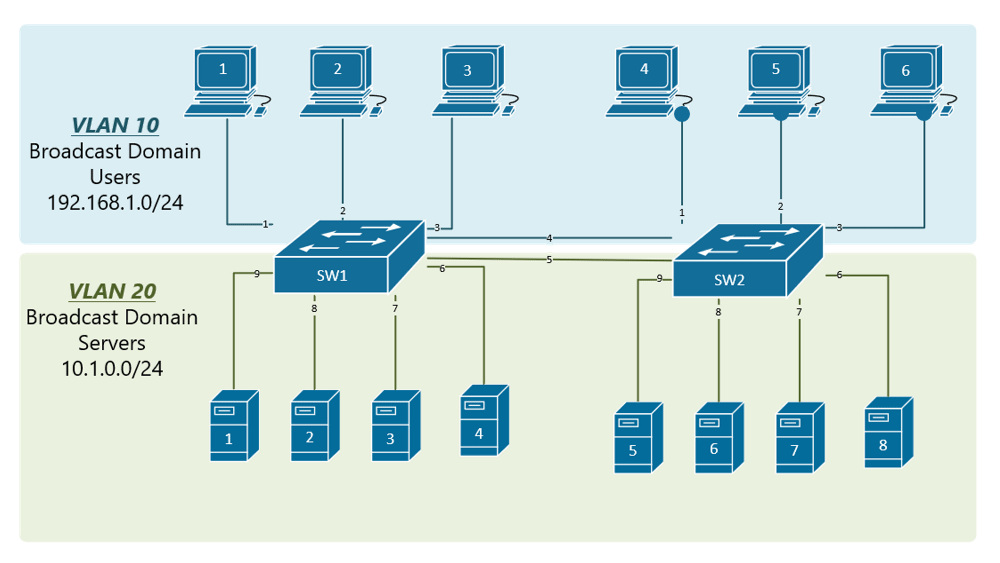
VLAN Translation, or 802.1Q Translation, is a technique used to modify the VLAN tag of a frame as it traverses a network. This is particularly useful in environments where the VLAN configuration needs to be changed as the frame moves from one network segment to another.
802.1Q Translation Process
In 802.1Q Translation, a network device, typically a switch or router, removes the original 802.1Q tag from the frame and replaces it with a new 802.1Q tag that is appropriate for the next network segment. This process is often used in inter-VLAN routing, where a frame needs to be forwarded from one VLAN to another.
Benefits of 802.1Q Translation
- Inter-VLAN Communication: 802.1Q Translation enables communication between different VLANs, even if they are not physically connected.
- VLAN Remapping: It allows for the remapping of VLAN IDs, which can be useful in network redesign or migration scenarios.
- Simplified Network Management: By translating VLAN tags, network administrators can simplify network management by reducing the need for complex routing configurations.
What is the difference between 802.1Q and ISL VLAN tagging?
+802.1Q and ISL are both VLAN tagging protocols, but they differ in their approach and functionality. 802.1Q adds a 4-byte tag to the Ethernet frame, which includes a 3-bit priority field and a 12-bit VLAN ID field. ISL, on the other hand, encapsulates the entire Ethernet frame within a new frame, including a 26-byte header and a 4-byte trailer. ISL is generally considered more robust and is used in large-scale networks, while 802.1Q is more commonly used in smaller networks.
How does Q-in-Q (802.1ad) VLAN stacking work?
+Q-in-Q (802.1ad) VLAN stacking allows multiple VLANs to coexist on the same physical link. It adds an outer 802.1Q tag to the frame, which carries the service provider’s VLAN ID, followed by the customer’s original frame, which may already have an inner 802.1Q tag with the customer’s VLAN ID. This allows the service provider to maintain separate VLANs for different customers while using a single link.
What is the purpose of VLAN Double Tagging (802.1Q-in-Q)?
+VLAN Double Tagging (802.1Q-in-Q) allows for the stacking of multiple 802.1Q tags within a single frame. It adds an outer 802.1Q tag with the service provider’s VLAN ID, followed by an inner 802.1Q tag with the customer’s VLAN ID. This technique is useful in virtualized environments where multiple VLANs need to coexist on a single link.
When is VLAN Translation (802.1Q Translation) used?
+VLAN Translation (802.1Q Translation) is used to modify the VLAN tag of a frame as it traverses a network. It is particularly useful in inter-VLAN routing, where a frame needs to be forwarded from one VLAN to another. It involves removing the original 802.1Q tag and replacing it with a new 802.1Q tag that is appropriate for the next network segment.



