12 Techniques To Master Metal Bending And Achieve Perfect Results

Metal bending is a captivating and challenging process that involves manipulating and shaping metal into desired forms. Achieving perfect results in metal bending requires a combination of skill, technique, and an understanding of the material's properties. Here, we explore 12 essential techniques that will help you master the art of metal bending and consistently produce exceptional outcomes.
1. Understanding Metal Properties

Before embarking on any metal-bending project, it is crucial to familiarize yourself with the properties of the specific metal you will be working with. Different metals exhibit unique characteristics, such as ductility, tensile strength, and heat conductivity, which directly influence their behavior during bending. For instance, aluminum is known for its excellent ductility, making it easier to bend and shape, while steel requires more force and precision due to its higher strength.
Key Considerations:
- Ductility: The metal’s ability to undergo plastic deformation without breaking.
- Tensile Strength: The maximum stress a metal can withstand before failure.
- Heat Conductivity: How quickly the metal can transfer heat, which affects its workability.
2. Choosing the Right Tools

Selecting the appropriate tools for metal bending is essential to ensure accuracy, efficiency, and safety. The choice of tools depends on the type of metal, the desired bend radius, and the complexity of the shape you aim to achieve. Here are some commonly used tools for metal bending:
Hand Tools:
- Bending Pliers: Ideal for making precise bends in small-scale projects.
- Pipe Benders: Designed for bending pipes and tubes with consistent radii.
- Hand Seamer: Useful for bending sheet metal into simple curves.
Power Tools:
- Hydraulic Press Brakes: Offer precise and consistent bending for sheet metal.
- Roller Benders: Perfect for bending large metal tubes and pipes.
- Power Hammer: Provides force and control for more complex bending tasks.
3. Marking and Measuring Accurately

Precision is key in metal bending, and accurate marking and measuring are fundamental to achieving perfect results. Before beginning the bending process, carefully measure and mark the metal to ensure that the bends are made in the correct locations. This step is crucial to maintain the integrity of the metal and prevent errors that could lead to material waste.
Marking Techniques:
- Use a scribe or a fine-tipped marker to make precise marks on the metal.
- For complex shapes, consider creating a template or pattern to guide your bends.
- Always double-check your measurements to avoid costly mistakes.
4. Heat Treatment Techniques

Heat treatment is often necessary to alter the metal’s properties and make it more malleable for bending. The specific heat treatment process depends on the type of metal and the desired outcome. For example, annealing is a common heat treatment technique used to soften metals and improve their ductility, making them easier to bend.
Heat Treatment Methods:
- Annealing: Heating the metal to a specific temperature and then slowly cooling it to alter its microstructure.
- Quenching: Rapidly cooling the metal to harden it, followed by tempering to reduce brittleness.
- Normalizing: Heating the metal and then air-cooling it to refine its grain structure.
5. Cold Bending vs. Hot Bending

Metal bending can be performed at different temperatures, each offering unique advantages and considerations. Cold bending involves shaping the metal at room temperature, while hot bending requires heating the metal to a specific temperature.
Cold Bending:
- Pros: Cost-effective, easy to control, and suitable for small-scale projects.
- Cons: May result in springback (rebound of the metal after bending), requiring additional force or a second bend.
Hot Bending:
- Pros: Reduces the risk of springback and allows for more complex shapes.
- Cons: Requires specialized equipment and expertise, making it more expensive.
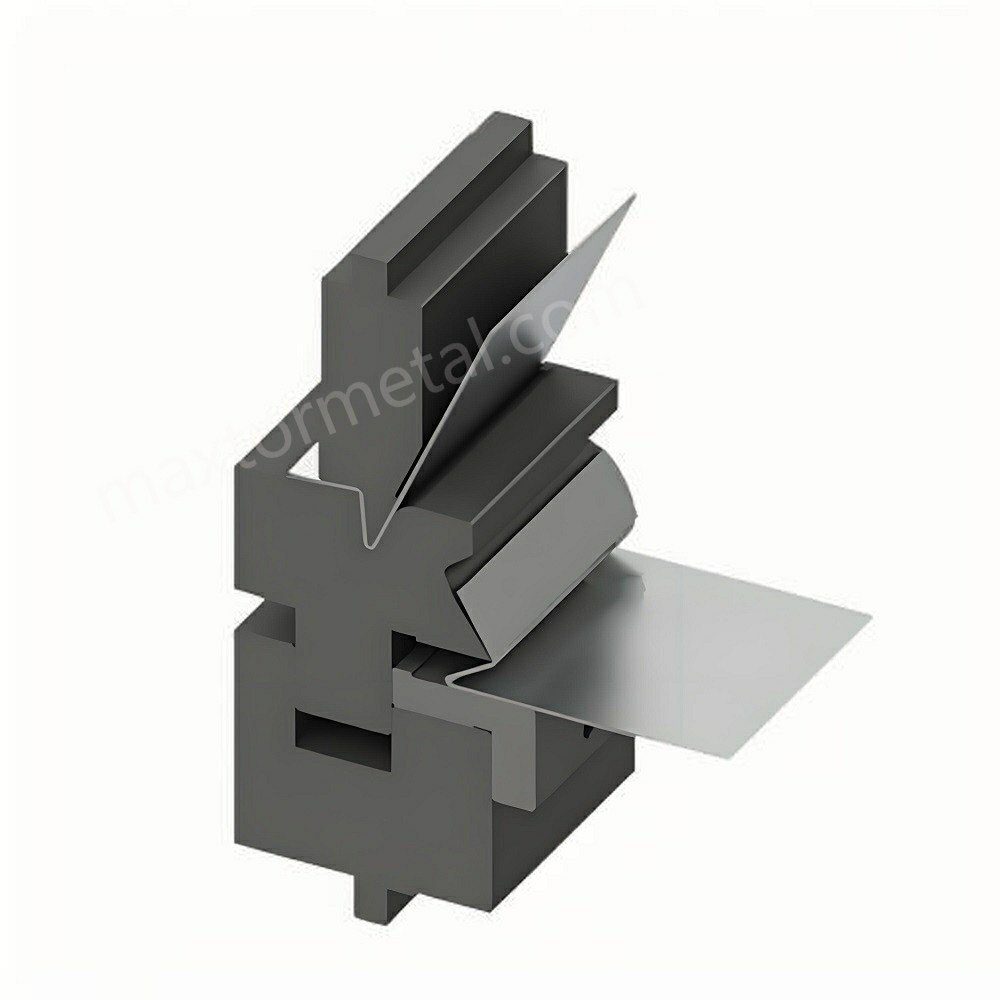
6. Master the Art of Forming Dies

Forming dies are crucial in metal bending, especially when working with complex shapes. These dies are custom-made tools designed to guide and support the metal as it is bent, ensuring precise and consistent results. Creating and using forming dies effectively can significantly enhance the quality of your metal-bending projects.
Forming Die Considerations:
- Choose the right material for your forming dies based on the metal you are bending.
- Design the die with the desired bend radius and shape in mind.
- Consider using multiple dies for complex shapes to achieve the best results.
7. Precision in Bend Radius and Angle

Achieving the desired bend radius and angle is critical to the success of your metal-bending project. Too much bending can lead to material failure, while insufficient bending may result in an incomplete shape. Maintaining precision in these aspects requires careful planning, accurate measurements, and the right tools.
Tips for Precision Bending:
- Use a bending radius chart or calculator to determine the appropriate bend radius for your metal.
- Consider using a bending mandrel or a form block to guide the metal and ensure a consistent bend.
- Practice and refine your technique to improve your accuracy over time.
8. Overcoming Springback

Springback is a common challenge in metal bending, especially when working with cold-bent metals. It occurs when the metal rebounds after bending, resulting in a less precise final shape. To overcome springback, you may need to apply additional force or consider using a springback calculator to determine the necessary correction angle.
Springback Reduction Techniques:
- Use a springback calculator to estimate the correction angle needed to compensate for springback.
- Apply annealing or stress-relief heat treatment to reduce the metal’s tendency to spring back.
- Consider using a forming die or a mandrel to support the metal during bending and minimize springback.
9. Preventing Cracks and Fractures
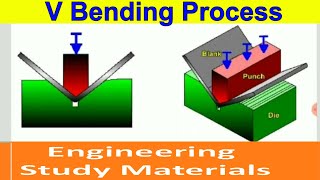
Cracks and fractures are potential hazards in metal bending, especially when working with brittle metals or applying excessive force. To prevent these issues, it is essential to understand the metal’s tensile strength and to avoid over-bending. Additionally, proper lubrication and the use of appropriate tools can help reduce the risk of cracks and fractures.
Prevention Strategies:
- Choose the right metal for your project, considering its tensile strength and ductility.
- Avoid sharp bends and gradual angles to minimize the risk of cracks.
- Apply a suitable lubricant to the metal to reduce friction and prevent cracking.
10. Surface Preparation and Finishing

The appearance and quality of your metal-bending project can be significantly enhanced through proper surface preparation and finishing techniques. This includes cleaning the metal, removing any impurities or contaminants, and applying a protective coating or finish to enhance its durability and aesthetics.
Surface Preparation and Finishing Tips:
- Clean the metal thoroughly before bending to remove any dirt or grease.
- Consider using a primer or a corrosion-resistant coating to protect the metal’s surface.
- For a professional finish, sand and polish the bent metal to achieve a smooth and glossy appearance.
11. Safety First
Metal bending can be a hazardous process if proper safety measures are not followed. It is crucial to prioritize safety throughout your projects to prevent accidents and injuries. This includes wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as safety glasses, gloves, and a respirator, especially when working with heat or hazardous materials.
Safety Guidelines:
- Always wear safety gear, including eye and respiratory protection, when working with metal.
- Keep a fire extinguisher nearby when using heat or performing hot bending.
- Be aware of the potential hazards associated with the specific metal you are working with and take necessary precautions.
12. Practice Makes Perfect
Mastering metal bending requires practice and patience. Even experienced metalworkers continue to refine their techniques and explore new methods. By experimenting with different metals, tools, and techniques, you can expand your skills and achieve increasingly complex and impressive results.
Tips for Continuous Improvement:
- Start with simple projects and gradually increase the complexity as you gain confidence.
- Seek feedback and advice from experienced metalworkers to refine your techniques.
- Stay up-to-date with the latest advancements and innovations in metal bending to stay ahead of the curve.
What is the best metal for beginners to practice bending techniques?
+For beginners, aluminum is an excellent choice due to its high ductility and ease of bending. It is a forgiving metal that allows for learning and refining bending techniques without the challenges posed by more rigid metals like steel.
Can I bend metal without specialized tools?
+While specialized tools make metal bending easier and more precise, it is possible to bend metal with basic hand tools. However, the complexity of the project and the desired accuracy may be limited without the use of specialized equipment.
How can I ensure consistent bend angles and radii in my projects?
+To achieve consistent bend angles and radii, invest in high-quality bending tools and forming dies. Additionally, practice your technique, measure accurately, and consider using a bending calculator or a bending chart to determine the appropriate bend parameters for your metal.



